
Annapolis and Arlington were essentially floating Comm Stations with massive
antenna arrays and extensive equipment installations
Annapolis had 48 HF transmitters ranging from 1kw AN/URT-23 to 40kw AN/FRT-40

|
Northampton and Wright were national command center ships (NECPA - National Emergency Command Post Afloat) and included extensive communications equipment and capability. While on station off the US East Coast, Northampton and Wright maintained contact with the shore via UHF troposcatter links to Lola (NC), Lewes (DE), and Cape Cod (MA). The tropo equipment may have been the AN/FRC-92 on shore and the AN/SRC-24 (REL 2500) shipboard- please send me e-mail if you have any info on this or anything related to these ships.
|
|||
|
Probably Lewes Delaware (Cape Henlopen, Ft. Miles) - original tropo antenna installation atop Battery
Hunter - photo from RM 3&2 manual |
Later Lewes, Delaware tropo antenna installation at Battery 519
Articles on Lewes - Delaware Outdoor Magazine and Coastalpoint More info
& photos on Lewes tropo antennas |
Later Lewes, Delaware tropo antenna installation at Battery 519 (thanks to Delaware State Parks) |
Lola (Cedar Island) NC - 32 ft tall conical pedestal is all
that remains of tropo relay antenna. |
Note - I've tried to select photos that show radio equipment and antenna installations
 USS Appalachian AGC-1 - 1944 |
 USS Appalachian AGC-1 - 1945 |
 USS Appalachian AGC-1 - 1945 |
 USS Appalachian AGC-1 - 1945-46 |
 USS Ancon AGC-4 - 1943 |
 USS Ancon AGC-4 - 1943 |
 USS Ancon AGC-4 - 1943 |
 USS Ancon AGC-4 - 1943 |
 USS Ancon AGC-4 - 1943 |
 USS Ancon AGC-4 - 1945 |
 USS Mount McKinley AGC-7 |
 USS Mount McKinley AGC-7 - 1950 |
 USS Eldorado AGC-11 - 1944 |
 USS Eldorado AGC-11 - 1944 |
 USS Estes AGC-12 Estes Info and Photo Page |
 USS Estes AGC-12 |
USS Teton AGC-14 - 1945
|
USS Adirondack AGC-15 1946
|
1945 Antenna Cable Plan pdf
- (AGC-15,-16, 17)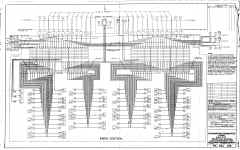
|
USS Pocono AGC-16 - 1957
|
USS Adirondack AGC-15 - 1952 
|

|

|
== |
USS Blue Ridge LCC-19 |
|||
|
Modern Blue Ridge and Mount Whitney photos and video |
USS Blue Ridge LCC-19 - 1977
|
USS Blue Ridge LCC-19 - 1980
|
|

|
 |
== | == |
| DESCRIPTION AND HISTORY OF USS BLUE RIDGE (LCC-19) Unlike her World War II predecessor of the same name, which had to be converted from a merchantman to an Amphibious Force Flagship, the new 620-foot UNITED STATES SHIP BLUE RIDGE represents a unique effort and achievement in the Navy's Command and Control ship design. Here for the first time is a platform built from the keel up to accomplish the mission of Command and Control coordination. In this 18,200 ton ship are found the facilities to direct and manage every phase of command and control operations. The BLUE RIDGE represents the accumulated knowledge of four decades of the Navy's experience in the difficult problem of Control and Coordination. Initially conceived in 1963, BLUE RIDGE was in the planning and design stage for four years before construction finally began at the Philidelphia Naval Shipyard in early 1967. Three and a half years later on 14 November 1970, she wvas commissioned. BLUE RIDGE utilizes her "main battery" of computers, communications gear, and other electronic facilities to fulfill her mission as flagship for the United States SEVENTH Fleet and her secondary function as a "command ship for the Amphibious Task Force and Landing Force Commanders during all phases of fleetwide operations." To maximize the Task Force and Landing Force Commanders' ability to effectively utilize the vast amount of incoming information, BLUE RIDGE has a Command and Control complex which is divided to give precise control of a certain aspect of the operation to a specific control module. At the heart of the Command and Control complex are two computer systems---the Naval Tactical Data System (NTDS) and the Amphibious Support Information System (ASIS). NTDS, through information provided by BLUE RIDGE radars, as well as through data links with other fleet ships, will provide a complete tactical picture of air, surface and subsurface contacts. From the NTDS picture the most expeditious and coordinated weapons assignments may be made to protect the Task Force from attack. ASIS allows commanders to have logistical information instantaneously. In addition to the two major computers mentioned above, an extremely refined communications system is also an integral part of the ship's radical new design. Through an automated patch panel and computer-controlled switching matrix, any combination of communications equipment desired may be quickly connected. The "clean" topside area is the result of careful design intended to keep the ship's interference to her own communications system at a minimum. A description of BLUE RIDGE would not be complete without mention of her twenty-knot plus speed capability. She is a great improvement in ship design, not only in speed, but also in habitability. Recreation rooms, air conditioning, ship's stores, spacious galleys and messing areas all help make life at sea a great deal more pleasant for the crew and embarked staffs. BLUE RIDGE has accommodations for 268 officers and 1200 enlisted men. |
|||
USS Mount Whitney LCC-20 |
|||

|
Modern Blue Ridge and Mount Whitney photos and video | 
|

|

|
Petty Officer 2nd Class Jeffrey Bennett, information systems technician, left, and Petty Officer 2nd Class Joseph Camino, information systems technician, observe the proper configuration of a high-frequency radio aboard the amphibious command ship USS Mount Whitney. Mount Whitney is the U.S. 6th Fleet flagship homeported in Gaeta, Italy, and operates with a hybrid crew of U.S. sailors and Military Sealift Command civil service mariners. | ||